1. Immunological Memory
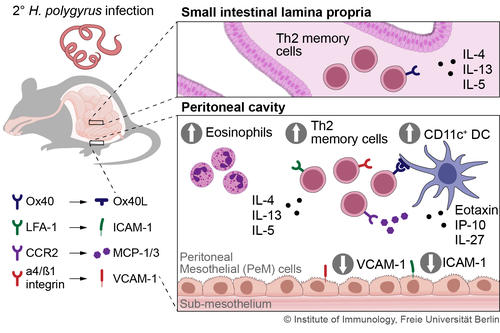
Fig.1 Overview of the distribution of Th2 memory cells in the small intestine and the peritoneum after primary infection and recruitment of the memory cells from the peritoneum after secondary infection with the small intestinal nematode H. polygyrus
Fig. 2 Immune responses in response to immunization with released nematode products (Yordanova et al. 2023)
1.1 Protective Immune responses
A protective immune response against nematodes is dependent on T helper cells of the type Th2, which produce the cytokines IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. In addition, helminth-specific IgG1 antibodies are of relevance for protection.
In infections with the small intestinal nematode H. polygyrus, we examined T helper memory cells after termination of the infection and showed that the Th2 memory cells persist in non-lymphoid organs, particularly in the peritoneum (Fig. 1). In the case of a challenge infection the Th2 memory cells are recruited from the peritoneum to mediate protection (Steinfelder et al., 2017, Yordanova et al., 2022).
Immunization with secreted-excreted products of nematodes, so-called ES products, lead to long-lived Th2 memory cells. These Th2 memory cells have a protective effect against reinfection, lead to an altered fecundity of the female worms and to cross-reactive T cells reactive against independent nematode infections (Fig. 2). Thus, immunization with nematode ES products induces the production of antigen-specific, protective Th2 memory cells in the host (Yordanova et al., 2023).
Selected publications:
- Yordanova, I. A.; Elizalde‐Velázquez, L. E.; Hartmann, S. (2023):Immunization with excretory‐secretory molecules of intestinal nematodes induces antigen‐specific protective memory Th2 cell responses. Eur J Immunol; 53(5), S. Article 2250237
- Elizalde‐Velázquez, L. E.; Yordanova, I. A.; Liublin, W.; Adjah, J.; Leben, R.; Rausch, S.; Niesner, R.; Hartmann, S. (2023):Th2 and metabolic responses to nematodes are independent of prolonged host microbiota abrogation. Para Immunol; 45(4 : Special Issue: Parasites and the Microbiota), S. Article e12957
- Yordanova, I. A.; Jürchott, K.; Steinfelder, S.; Vogt, K.; Krüger, U.; Kühl, A. A.; Sawitzki, B.; Hartmann, S. (2022): The host peritoneal cavity harbors prominent memory Th2 and early recall responses to an intestinal nematode. Front Immunol.; 13, S. Article 842870
- Steinfelder, S., S. Rausch, D. Michael, A. A. Kühl, S. Hartmann.2017. Intestinal helminth infection induces highly functional resident memory CD4+ T cells. Eur J Immunol, 47:353-363; doi:10.1002/eji.201646575.
Third-party funding: DFG Individual Research Grant: S. Hartmann
1.2 Nematode products and influence on infection-independent inflammatory processes
The secreted-excreted products of nematodes, the ES products, not only lead to long-lived Th2 memory cells, but also have immunomodulatory properties and have an impact on other infection-independent inflammatory diseases. For example, we were able to demonstrate a significant suppressive effect on the development of allergic diseases by secreted nematode molecules (Schnöller et al,. 2008; Daniłowicz-Luebert et al, 2013; Whelan et al, 2014; Ebner et al, 2014; Ziegler et al, 2015; Ebner et al, 2021). The long-term aim is to use these immunoregulatory components of nematodes to regulate independent chronic inflammatory diseases.
Selected publications:
- Ebner, F.; Lindner, K.; Janek, K.; Niewienda, A.; Malecki, P.H.; Weiß, M.S.; Sutherland, T.E.; Heuser, A.; Kühl, A.A.; Zentek, J.; Hofmann, A.; Hartmann, S. (2021): A helminth-derived chitinase structurally similar to mammalian chitinase displays immunomodulatory properties in inflammatory lung disease. J. Immunol. Res., DOI: 10.1155/2021/6234836
- Ziegler, T., S. Rausch, S. Steinfelder, C. Klotz, M.R. Hepworth, A. Kühl, P-C- Burda, R. Lucius, S. Hartmann. 2015. A novel regulatory macrophage (Mreg) induced by a helminth molecule instructs IL-10 in CD4+ T-cells and protects against mucosal inflammation, J. Immunology, 194:1555-1564.
- Whelan, R., S. Rausch, F. Ebner, J. Richter, N. Hering, D. Günzel, J.-D. Schulzke, A. Kühl, P. Janczyk, K. Nöckler, L. Wieler, S. Hartmann. 2014. A novel therapy via a transgenic probiotic secreting a parasite immunomodulator for site-directed treatment of gut inflammation. Molecular Therapy, 22:1730-1740.
- Ebner, F., M. R. Hepworth, S. Rausch, K. Janek, A. Niewienda, A. Kühl, P. Henklein, R. Lucius, E. Hamelmann, S. Hartmann. 2014. Therapeutic potential of larval excretory, secretory proteins of the pig whipworm Trichuris suis in allergic disease. Allergy, 69:1489-1497.
- Daniłowicz-Luebert, E., S. Steinfelder, A. Kühl, G. Drozdenko, R. Lucius, M. Worm, E. Hamelmann, S. Hartmann. 2013. A nematode immunomodulator inhibits grass pollen-specific allergic responses by controlling excessive Th2 inflammation. Int. J. Parasitol., 43:201-210.
- Schnöller, C., S. Rausch, S. Pillai, A. Avagyan, B. Wittig, C. Loddenkemper, A. Hamann, E. Hamelmann, R. Lucius, S. Hartmann. 2008. A helminth immunomodulator reduces allergic and inflammatory responses by induction of IL-10-producing macrophages. J. Immunol., 180: 4265-4272.
Third-party funding: BMBF “Validierung innovativen Potentials“, S. Hartmann